We have spoken with subscribers and reassessed the Real Asset Chartbook; many people have commented that it is a fire hose of information, rather than a succinct delivery of a few key points in the world of liquid real assets. As such, we will pivot slightly to see if the product, delivered differently, is more appealing. The PDF Chart Book, which contains all the information we use at Massif Capital on a day-to-day basis, is still available at the bottom.
This Week's Key Take Aways
The gold-to-oil ratio may be telling us something about the inflation outlook
Copper mining challenges swing market to potential 2025 deficit
Stock-specific risk in US industrials is on the rise, and YTD industrial outperformance of SPX might come to an end
Chinese action to address the lithium oversupply appears insufficient
Shiny Rock Demands More Respect Than Black Gold

The gold-to-oil price ratio surged above 50x this week, signaling growing inflation anxiety stemming from US tariff policies. At 55.5x in May—the second-highest peak historically—the ratio suggested markets were anticipating structural rather than cyclical inflation, and it still appears to be the case today. The ratio has remained elevated for over three years, far exceeding typical bottom-to-peak cycles of under two years seen in 2008-09, 2014-16, and 2018-2020. With US Core PCE rising to 2.6% in Q2 from 1.3% in Q1 and WTI oil 13.6% higher over three months, the divergence reflects investors' hedge against tariff-driven cost pressures. This backdrop supports gold's continued outperformance during Trump's second term.
Why equity investors should care: The extreme gold-oil ratio has historically coincided with recessions, suggesting that inflation hedges may outperform traditional risk assets in the current policy environment.
Relevant tickers: GLD, GOLD, NEM, AEM, USO, XLE, XOM, CVX
Copper's Perfect Storm as Mine Disruptions Threaten Balanced Market
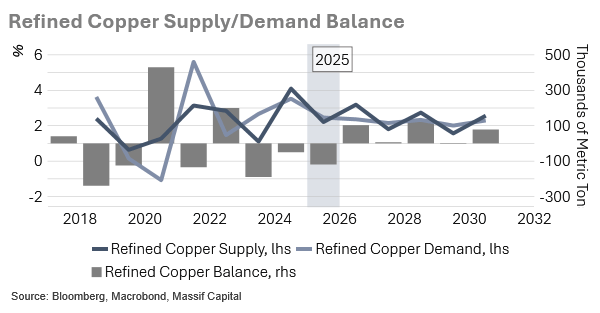
The copper market shifted from balanced to deficit this week as mounting mine disruptions culminated in Codelco's suspension of El Teniente operations following a fatal tunnel collapse. Total 2025 disruptions now approach 1.3 million tons, with seismic events exposing design flaws in aging underground operations. Codelco alone faces another 1% output decline after stabilizing in 2024, while Ivanhoe cut Kamoa-Kakula guidance by 155,000 tons due to seismic activity. These disruptions, combined with grade deterioration at major mines like Grasberg and Collahuasi, have forced a revision in supply forecasts from 3% growth to a 0.5-1% decline.
Why equity investors should care: The shift to a market deficit combined with smelter bottlenecks creates structural supply constraints that should support copper prices and benefit miners with stable, low-cost operations.
Relevant tickers: FCX, SCCO, IVN, TECK, BHP, RIO, LUN, HBM, and many others
Industrial Earnings Volatility Hits Historic Extremes Amid Margin Pressure
Charts from GS: Blue bars are Q2’25 spread of realized volatility vs. implied (higher = the stock moved more than expected, lower = it moved less than expected). Orange bars last 12 quarters median spread of realized vs. implied volatility. Both Charts are of US Industrials MktCap > $50 bn

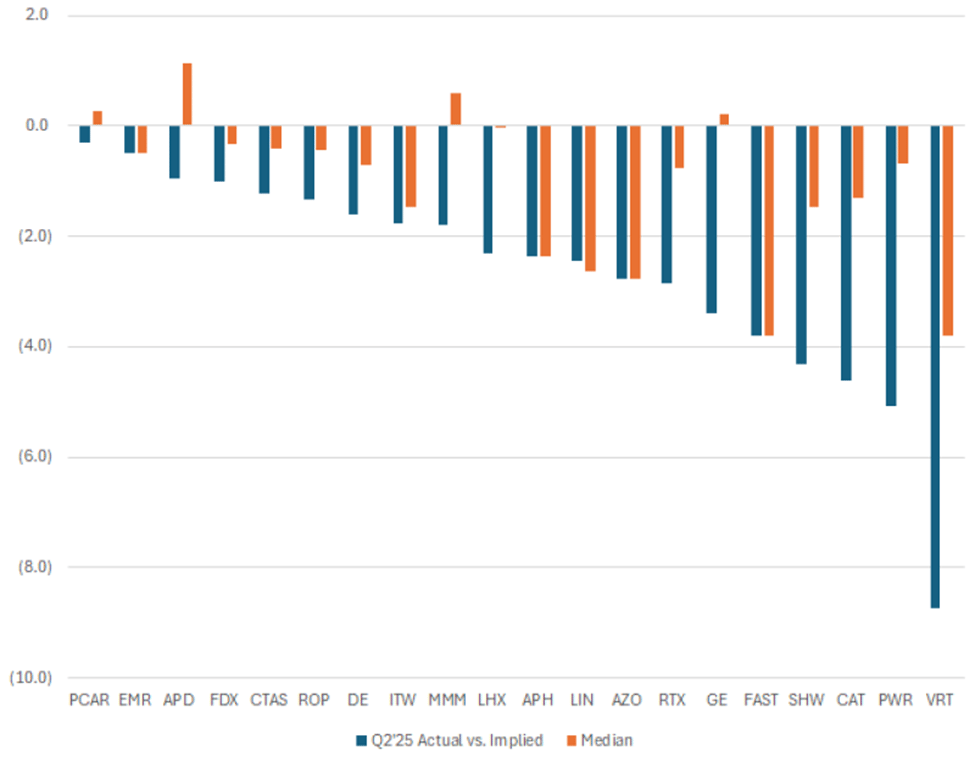
The industrial earnings season concluded with unprecedented volatility as companies navigated the impacts of tariffs and margin compression, with realized volatility significantly exceeding implied moves across multiple market capitalization segments. The largest companies exhibited the most dramatic swings, with TEL, TDG, and GEV experiencing moves that exceeded options-implied expectations. Consensus forecasts, according to Bloomberg, now project that S&P 500 gross margins peaked in Q2, with a 101-basis-point decline expected before recovery in 2026.
Non-technology stocks face particularly acute pressure, with margins expected to drop 151 basis points through year-end and showing limited recovery prospects. The earnings concentration risk has intensified, with just 13.1% of technology companies and 14.4% of non-technology companies effectively driving their sectors’ earnings.
Why equity investors should care: Historic earnings volatility, combined with margin compression, suggests increased stock-specific risk and potential for significant opportunities for stock pickers as tariff impacts materialize in 2H earnings.
Relevant tickers: CAT, ETN, ROK, EMR, GEV, MMM, ITW, DOV
US Construction Spending Collapse Signals Possible Industrial Metal Reckoning

US construction spending accelerated its decline this week, matching pandemic-era velocity and exposing the disconnect with industrial metals pricing and equity valuations. The Bloomberg Industrial Metals Index, which has been closely correlated with construction spending (and the S&P 500) since 2015, suggests that either metals are overvalued or that equities face reversion risk.
Why equity investors should care: The correlation between construction spending and industrial metals suggests significant downside risk for materials stocks if normal mean reversion patterns reassert themselves.
Relevant tickers: X, CLF, NUE, STLD, AA, FCX, SCCO
Industrial Sector Gains Under Pressure Amid Manufacturing Headwinds and Resistance in XLI/SPY Ratio

YTD, the XLI is up 16.08% vs. the SPY 8.9%, though the industrial sector faces headwinds from manufacturing contraction persisting since late 2022. Based on the ratio analysis in the chart above, the XLI may continue to underperform the SPY. The ratio appears to have key resistance confirmed by multiple retracements.
Why equity investors should care: Equity investors should monitor XLI's relative performance to SPY as industrial sector rotation could signal broader economic shifts affecting cyclical versus defensive positioning across portfolios
Relevant tickers: GEV, CAT, D, ITW
China's Memo to Lithium Producers Goes Unread as Involution Fails to Sustain Lithium Rally
China's much-heralded "anti-involution" policies aimed at curbing destructive price competition across commodity sectors showed mixed results this week, with lithium prices retreating from initial gains despite government intervention. Lithium carbonate prices jumped to 80,000 yuan per ton in July from below 60,000 yuan in June on regulatory actions, including mining suspensions at Zangge Mining and maintenance at Jiangxi Special Electric Motor.
However, these suspensions represented less than 2% of 2024 output, and improved margins prompted producers to increase capacity utilization above 58%, pushing July output to a record 80,000+ tons. The fundamental challenge remains: unlike steel production, dominated by state-owned enterprises, lithium is primarily controlled by private companies driven by cash flow rather than government guidance. Inventories climbed to 142,000 tons. Elsewhere in the Li-ion battery supply chain, overcapacity also persists, with battery cell manufacturing overcapacity ratios climbing to 252% in 2025 and exceeding 300% by 2028.
Why equity investors should care: The failure of soft policy intervention suggests continued oversupply pressures in Chinese commodity markets, particularly affecting lithium and battery material suppliers exposed to margin compression.
Relevant tickers: ALB, SQM, LTHM, LAC, LAR
And, just in case you still want the fire hose of information:
Until next week,
